Bookkeeping
Direct material variance definition
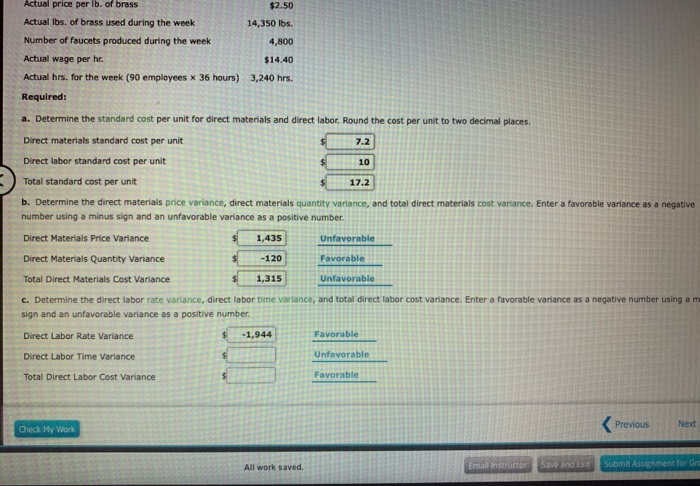
This is a favorable outcome because the actual quantity of materials used was less than the standard quantity expected at the actual production output level. As a result of this favorable outcome information, the company may consider continuing operations as they exist, or could change future budget projections to reflect higher profit margins, among other things. Figure 8.3 shows the connection between the direct materials price variance and direct materials quantity variance to total direct materials cost variance. Figure 10.35 shows the connection between the direct materials price variance and direct materials quantity variance to total direct materials cost variance. Materials price variance (or direct materials price variance) is the part of materials cost variance that is attributable to the difference between the actual price paid and the standard price specified for direct materials. In this case, the actual price per unit of materials is $9.00, the standard price per unit of materials is $7.00, and the actual quantity purchased is 20 pounds.
If a company’s actual quantity used exceeds the standard allowed, what would the variance be?
Materials price variance represents the difference between the standard cost of the actual quantity purchased and the actual cost of these materials. Keep in mind that the standard cost is the cost allowed on the good output. Putting material, labor, and manufacturing overhead costs into products that will not end up as good output will likely result in unfavorable variances. Supplier performance also plays a crucial role in direct material variance. Reliable suppliers who consistently deliver quality materials at agreed-upon prices help maintain stable production costs. Conversely, issues such as late deliveries, substandard materials, or unexpected price hikes can lead to variances.
6 Direct Materials Variances
We can also see that this is a favorable variance just based on the fact that we paid $5.60 per board food for our materials instead of the $6 that we used when building our budget. If a budget variance is unfavorable but considered controllable, then perhaps there is something management can do immediately to rectify the problem. If the budget item is not something management directly controls, then perhaps they need help crafting a new business strategy in order to survive and grow. The first question to ask is “Why do we have this unfavorable variance of $2,000? ” If it was caused by errors and/or inefficiencies, it cannot be assigned to the inventory. Errors and inefficiencies are never considered to be assets; therefore, the entire amount must be expensed immediately.
Advanced Techniques in Variance Analysis
This is an unfavorable outcome because the actual price for materials was more than the standard price. As a result of this unfavorable outcome information, the company may consider using cheaper materials, changing suppliers, or increasing prices to cover costs. The direct materials variances measure how efficient the company is at using materials as well as how effective it is at using materials. There are two components to a direct materials variance, the direct materials price variance and the direct materials quantity variance, which both compare the actual price or amount used to the standard amount. In a manufacturing company, the purchasing and accounting departments usually set a standard price for materials meeting certain engineering specifications.
How is the direct material quantity variance calculated?
- By understanding these trends, companies can anticipate future variances and take proactive measures to mitigate them.
- To compute the direct materials price variance, subtract the actual cost of direct materials ($297,000) from the actual quantity of direct materials at standard price ($310,500).
- That inefficiency will likely cause additional variable manufacturing overhead which will result in an unfavorable variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance.
- It isdefined as the difference between the actual quantity of materialsused in production and budgeted materials that should have beenused in production based on the standards.
Variances are calculated and reported at regular intervals to ensure the quick remedial actions against any unfavorable occurrence. Premium Furniture, a US based Inc., uses a standard costing system to control its direct materials and conversion operating cash flow calculation costs. During the month of December 2022, its workers used 3,750 feet of timber to finish 1,500 office chairs. The standard length of timber allowed to manufacture an office chair is 2.75 feet and the standard rate per foot of timber is $3.50.
Manufacturing overhead
The standard materials cost of any product is simply the standard quantity of materials that should be used multiplied by the standard price that should be paid for those materials. Actual costs may differ from standard costs for materials because the price paid for the materials and/or the quantity of materials used varied from the standard amounts management had set. These two factors are accounted for by isolating two variances for materials—a price variance and a usage variance. In this case, the actual price per unit of materials is $6.00, the standard price per unit of materials is $7.00, and the actual quantity purchased is 20 pounds.
We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. We will pursue the interdependence of variances in the following examples.
An efficiency variance measures how well the business is using materials and human resources—in other words, the efficiency variance tracks the efficiency of the conversion process. During the month of March, the following quantities of materials were sent to the factory and 32,340 tons of product K was actually produced. Using the materials-related information given below, calculate the material variances for XYZ company for the month of October.
An unfavorable outcome means you spent more on the purchase of materials than you anticipated. With either of these formulas, the actual quantity used refers to the actual amount of materials used at the actual production output. The standard quantity is the expected amount of materials used at the actual production output. If there is no difference between the actual quantity used and the standard quantity, the outcome will be zero, and no variance exists.